Dialysis is a treatment that regulates the function of your kidneys when your organs stop working.
If your kidney disease is severe and your body can’t work properly to support you, you may need dialysis. (Image credit: Science Image Library/Getty Images).
Your kidneys are part of your urinary system. These two bean-shaped bodies are located below the ribs on either side of the spine. It removes waste and fluid from the body, regulates blood pressure and strengthens bones. They make sure your blood contains minerals like potassium and sodium (salt). Finally, they produce hormones that cause the body to make red blood cells.
Who needs dialysis?
If your kidney disease is severe and your body can’t work properly to support you, you may need dialysis or a kidney transplant. Injury or medical conditions such as lupus, high blood pressure or diabetes can cause kidney disease. For unknown reasons, you may develop kidney disease.
Dialysis is usually started when symptoms or laboratory tests show high levels of toxins in the blood. Symptoms of kidney failure include nausea, fatigue, bloating and vomiting.
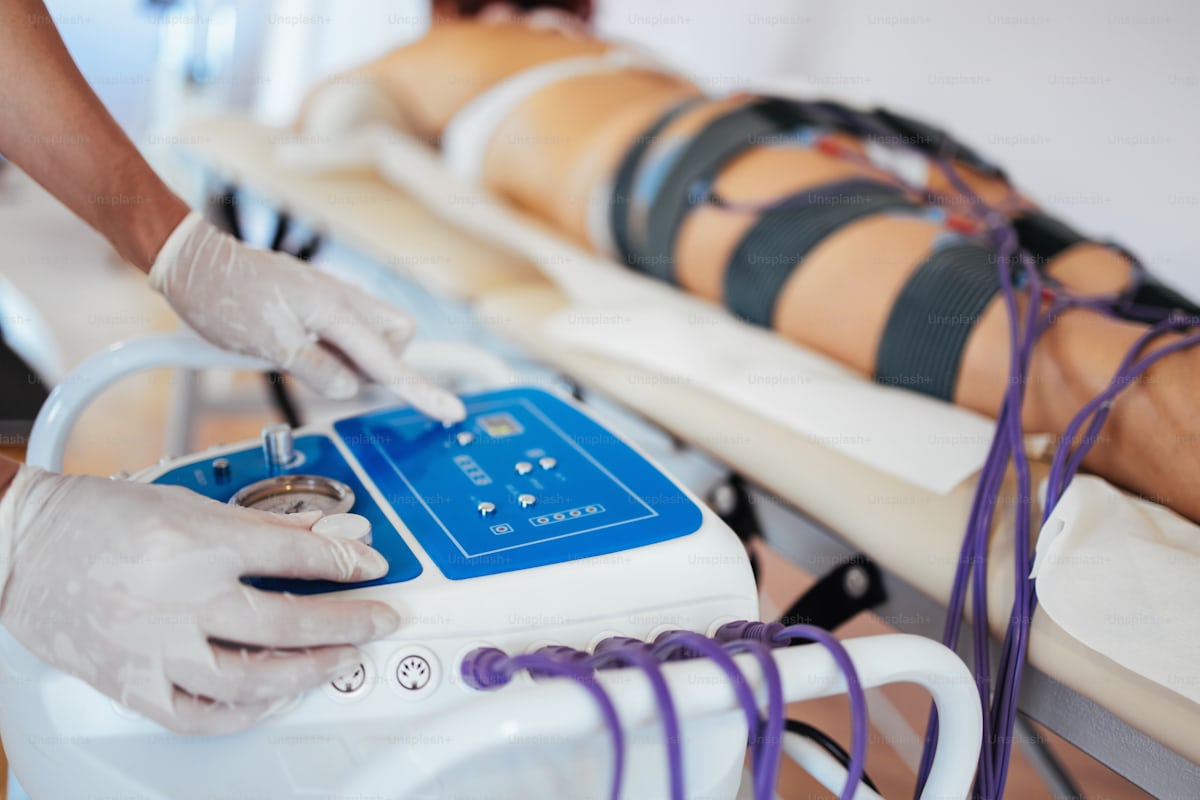

When to start dialysis depends on your age, energy level, overall health, lab test results, and how well you are following your treatment plan. Although it will make you feel better and live longer, it will take a lot of your time.
There are five stages of kidney disease. In stage five, you are considered to have end-stage renal disease or kidney failure. It occurs when the kidneys are functioning at 10-15% of normal. You may need dialysis or a kidney transplant to survive. You can receive dialysis while waiting for a transplant.
Your doctor will tell you when to start treatment. They will explain to you which type is best for you.
Type of dialysis
There are two main types of dialysis:
Dialysis: Taking blood from the body through a filter, purifying it, and returning it to you. This is done at a dialysis facility or at home.
Potential risks of this type of dialysis include infection, poor circulation, scar tissue blockage, blood clots, anemia and sudden heart failure.
Peritoneal Dialysis: Blood is filtered in the body. A special fluid is injected into your stomach to remove waste from the blood flowing through the small blood vessels in your stomach. Then remove the liquid. This type of dialysis is usually performed at home.
Risks of this type of dialysis include skin infections around the catheter and an infection called peritonitis, which can occur when the catheter enters your abdomen. Tubes and fluid in the abdomen weaken the abdominal muscles and can cause a hernia. This type of dialysis can also cause weight gain.
Continuous renal replacement therapy is a type of dialysis performed in the intensive care unit to save the lives of patients who cannot tolerate regular dialysis. Do this 24 hours a day, slowly and continuously removing waste and fluid.
Haemodialysis
In dialysis, a machine removes blood from the body. Your blood is then filtered by dialysis (artificial kidney) and the purified blood is returned to your body. This process lasts 3-5 hours.
You can get tested three times a week at a hospital or dialysis center.You can also receive dialysis treatment at home. Indoor baths allow you to bathe longer or more frequently – usually three to seven times a week. You can do this at night so you can sleep when it happens.
How does dialysis work?
Dialysis: During dialysis, the blood is passed through a special machine called a dialyzer. This device removes waste products and excess fluid from the blood before it enters your body. You can receive dialysis treatment at a nephrology clinic or at home.Blood is drawn through the needle and returned to your body, usually in your arm, neck or leg.
Peritoneal dialysis
During peritoneal lavage, fluid is drained into the peritoneal cavity. Fluid flows in and out of the catheter. A catheter is a thin, flexible tube about 30 cm long that is always kept in place.Waste products from the blood enter the fluid in the peritoneal cavity.
It is then removed from your body. Peritoneal dialysis can be done daily at home.Guidelines (Continuous Outpatient Peritoneal Dialysis)Use an automatic washing machine.

Dialysis life
Although starting dialysis is a life-changing event, it is still possible to lead an active life. However, your life may look different before dialysis.
The right type of dialysis depends on:
How to live your life
They are watching
Your skills
If you have a caregiver
Where do you live
Dialysis is an ongoing treatment. It is important not to miss a dialysis session. Dialysis can usually be done overnight at home. Depending on your needs, you may need to have dialysis several times a day.
Reference
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/14618-dialysis
https://www.davita.com/treatment-services/dialysis/what-is-dialysis-and-when-do-i-start
https://www.webmd.com/a-to-z-guides/kidney-dialysis
https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/dialysishttps://www.freseniusmedicalcare.ae/en-ae/patients-families/understanding-dialysis
https://www.kidney.org.uk/know-your-numbers-dialysis
https://www.webmd.com/a-to-z-guides/kidney-dialysis
https://www.davita.com/treatment-services/dialysis/what-is-dialysis-and-when-do-i-start
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK563296/
https://www.kidney.org/kidney-topics/hemodialysis
 using WordPress and
using WordPress and
Comments are closed